- HanJin
What happens if you fly a drone above 400 feet? The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is restricting the use of drones for commercial purposes to a height below 400 feet in a bid to avoid collisions with aircraft.
In April 2016, the FAA mandated that drones operated by the US government cannot fly higher than 400 feet for security reasons. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has restricted the use of drones for commercial purposes to a height below 400 feet in a bid to avoid collisions with aircraft.
In this article, we will explain this clearly to you.
Table of Contents
- 1 What Are The Part 107 Rules?
- 2 What are the laws regarding flying high-altitude drones?
- 3 How To Fly A Drone?
- 4 Important Methods for Drone Piloting
- 5 Important Things to Keep in Mind Before Flying Your Own Drone
- 6 What Happens If You Fly A Drone Above 400 Feet
- 7 Can A Drone Be Flown Above 400 Feet Legally?
- 8 What Are The Penalties For Flying Your Drone Above 400 Feet?
- 9 FAQs
- 10 Conclusion
What Are The Part 107 Rules?
Part 107 of the Federal Aviation Regulations is a set of rules and regulations that govern the operation of small unmanned aircraft systems (sUAS) for commercial purposes in the United States. These rules were developed by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in response to the increasing use of drones for a variety of commercial applications, including aerial photography, mapping, and inspection.
Under Part 107, anyone operating a drone for commercial purposes must obtain a Remote Pilot Certificate, which involves passing an aeronautical knowledge test and completing a TSA security screening. This certification ensures that pilots have the necessary knowledge and training to operate drones safely and responsibly.
Part 107 also includes operational limitations for drone flights, such as the requirement to fly below 400 feet above ground level, and to maintain visual line-of-sight with the drone at all times. Drones must also yield the right of way to other aircraft and cannot be operated over people or moving vehicles without meeting certain conditions.
Additionally, Part 107 mandates that drones be registered with the FAA and display their registration number on the aircraft. This helps to ensure that drones can be traced back to their owner in the event of an accident or other incident.
By following the regulations set forth in Part 107, drone pilots can help to ensure that their flights are conducted safely and in compliance with federal laws. These rules are designed to promote the safe and responsible use of drones while minimizing the risk of accidents and collisions with other aircraft.
What are the laws regarding flying high-altitude drones?
The FAA has listed the rules and regulations for high-altitude drones that must be followed in all situations.
- You must ensure that your drone is kept below 400 feet in Class G uncontrolled airspace.
- To fly in controlled airspaces, Class B, C, D, and E, you will need authorization waivers. You can obtain authorization from LAANC or NoDroneZone. Or any written agreement with Federal Aviation Administration.
- Even if you have been given permission to fly near manned aircraft, it is a violation of safe airspace.
- Fly your commercial or recreational drone in a suspicious manner and avoid flying over people.
- For authorization to avoid height restriction, you can also take the Part 107 licensing test
- Before you fly your drone in controlled or uncontrolled airspace, register it with the FAA.
How To Fly A Drone?

1. Secure an open area for practice
If you presently possess a drone or are thinking of buying your own, then you probably already have an area in your mind for training. It may be almost any open outdoor space, so long as it is secure and free of obstacles so that you do not wind up crashing the drone into a tree, wall, or perhaps even other men and women. Additionally, ensure the location permits the use of drones not to violate any laws.
2. Position the drone
First of all, find a fantastic takeoff place. Then, be sure that the drone is positioned based on this documentation ideally before you and onto a level surface, together with you and the drone facing the same direction. Please do this before each flight, and do not try to do it differently unless you have gained sufficient confidence and expertise in flying your drone.
3. Connect the transmitter into the drone
There is yet another thing that you will want to recall before takeoff: sequencing. We begin with the measures which will require training.
Right before you turn to the transmitter, then push the throttle mode down. Next, switch the transmitter, then connect the drone’s battery. This is a critical sequence that you will need to follow both before shooting off and after landing. Then, following your flying session, follow the reverse sequence steps: disconnect your drone’s battery and turn off the transmitter.
- Before Takeoff After Landing
- Push throttle down way
- Turn transmitter ON
- Connect drone’s battery
- Disconnect drone battery
- Turn transmitter OFF
4. Exercise takeoff and landing
After following the preceding steps for preparation before takeoff, you will gradually push the throttle (left stick) upward and observe the drone lift away. Please keep it in position without moving ahead or into the sides with the roll and roll orders (right stick).
When you’ve successfully found the drone several feet above the floor, attempt to land it smoothly as possible, keep it stable and gradually push the throttle (left stick) this time till it reaches precisely the identical place on the floor.
5. Practice hovering

The next thing you are going to be practicing is hovering. Lift off (measure 5) a couple of feet above the floor and maintain the drone as steadily as possible. It’ll seem pretty dull for first-timers since it takes concentration, but practicing this will help improve your flying abilities (particularly at the beginning and finish of your flying periods ) and maintain your drone security.
Concentrate on controlling these basic maneuvers (remove, balancing, and landing) first since it can allow you to have a simpler time implementing more complex flying techniques in the future.
6. Practice rotating
One other important thing you will have to be familiar with is the turning of the drone working with the left stick’s yaw control. First, launch the drone, place it, then gradually push the left bar left or right before the drone rotates to confront you.
Many find it hard at first as you will need to pay close attention to this drone’s orientation, especially where its front and rear are, but the experience indeed makes it more accessible.
To assist you in flying the drone regardless of where it is confronting, make a mental image of you being within the drone and flying. This is how seasoned professionals remain on track, however far the drone spins and turns and assists them to envision the way they ought to fly the drone to attain winning aerial photographs.
If you still do not get it on your fifth attempt, do not worry. Many do not get it on their tenth. What is important is that you’re slowly (but surely!) Becoming popular in controlling the way the drone acts.
7. Exercise These Beginner Drone Approaches

Now that you have heard all the basic controls and maneuvers, it is time to unite all your gained knowledge and expertise into a single session. That is also where you will eventually get to use the ideal stick to transfer the quadcopter. Listed below are a couple of sample controls and motions Which You Can Try after the drone is in the atmosphere:
Traveling in parallel avenues by transferring the drone forward and backward with the pitch control (right stick) and then left and right with the roster control (right bar)
Draw a square with the pitch and roll controls (right stick)
Fly forward and backward into a parallel path with the drone facing the course of this flight by transferring the drone forwards with the pitch controller (right stick), stopping, rotating the drone 180 degrees until It’s facing you, and moving the drone forwards again till it reaches its original position
Draw a square by moving the drone forwards with the pitch controller (right stick), stopping, rotating the drone 90 degrees to the left or directly using the yaw controller (left bar), and replicating three measures before the drone returns to its original position
Draw a circle with the yaw controller (left stick) and pitch controller (right bar)
Draw a figure using the yaw controller (left stick) and pitch controller (right bar)
Important Methods for Drone Piloting
While drones may look like toys, even if misused, they can damage property and even harm people or creatures. Learning how to control a drone safely and correctly is essential to being a responsible pilot.
1. Get used to the controls
We have clarified the primary controls on your transmitter, but this is not enough. At some point, you ought to get used to your power until you do not need to look down on it every couple of seconds.
Comparable to playing a video game control, you will want to practice before you can”forget” your power and concentrate on this mental image of you being the pilot. In this manner, you can do different maneuvers as readily as you can move your limbs and focused on attaining a well-composed high-resolution aerial vision.
The chart below demonstrates how the propellers act during every motion to understand better how your quadcopter can move in particular directions.
2. Maintain the drone near
Now, it is normal for any beginner to become enthusiastic about putting their new skills into practice. However, while you’re at it, be sure that you keep the drone near enough (and within sight). In addition, you should learn your drone’s limitations, especially the conclusion of its transmission range, since you do not need the control to eliminate communication with the aircraft.
Some innovative drones can come back and landing on their own when they get out of range. However, there is no guarantee the drone will have the ability to keep itself protected from obstacles throughout auto-landing. The most effective method is to maintain it indeed close enough for you to have the ability to make out the drone’s orientation about a position.
Important Things to Keep in Mind Before Flying Your Own Drone

1. Charge the battery
You will require an ultimately charged battery to enjoy heavy flights. Be sure you use just the charger and battery which came with your drone. If you would like to bring backup batteries, make sure of their compatibility before using them along with your drone.
2. Register Your Drone
The upcoming important issue to consider is to enroll your remote-controlled aircraft in some sUAS (little unmanned aircraft program ) weighing between 0.55 and 55 lbs together with all the FAA and mark it with a registration number. These drone enrollment needs to help hold owners accountable if they end up damaging electricity lines or inducing any injury with their aircraft.
Registering drones using the FAA is as simple as making an account on their site, though you can opt to enroll by newspaper too. It’ll cost you a minimum fee but enrolling today will cover the subsequent three (3) years. Check out the video below to find step-by-step directions on How Best to enroll your drone together with the FAA:
3. Get to Know the Rules and Regulations
For everyone’s security, such as your own, it is crucial that you abide by regulations set for recreational drones. Listed below are the basic principles which you will want to follow along with every single time you fly your drone to get pleasure.
- Stay under 400 feet
- Keep flight rate at or under 100 miles
- Fly just during daytime
- Aircraft should weigh under 55 Pounds
- Yield right of way to manned aircraft in Any Way times
- Keep aircraft in line of sight in Any Way times
- Fly according to community-based guidelines
- Notify airports and air traffic management before flying over five miles of the airport
- Don’t fly humans
- Don’t fly out of a moving automobile
4. Download “No Fly” Programs
As you might already know, you will find places in each state where drones aren’t permitted to fly. These are known as”no fly” zones, and breaking the rules can get you fined. In addition to that, there is also the weather to worry about.
Luckily, there are programs that you can download to locate and watch out for all these “no fly” zones. You can quickly look for lists of reliable apps for your project, or you can immediately check out the following:
B4UFly – FAA-developed program for signaling fly/no-fly requirements and much more.
UAV Forecast – A fantastic alternate for your B4UFly provides detailed information on weather conditions in particular areas from a tiny aerial vehicle standpoint.
Hover – Great for beginners who need simple screens of real-time weather reports and fly zones (along with a fly/no-fly index ), in addition to a flight log for recorded flight information.
Tesla Field Recorder is useful for detecting, measuring, and documenting magnetic disturbances that may disturb flight operations.
Rather than asking yourself or others if you’re able to fly your drone in a particular area, it is possible to discover the answers directly on your cellular device.
5. Read the Instruction Manual
One thing you absolutely shouldn’t miss would be to read the documentation. From the drone’s bodily down parts to its flight features, familiarize yourself with everything that you will need to understand to minimize problems and inconveniences in the future.
What Happens If You Fly A Drone Above 400 Feet

What Is The Basis For The 400-foot Rule?
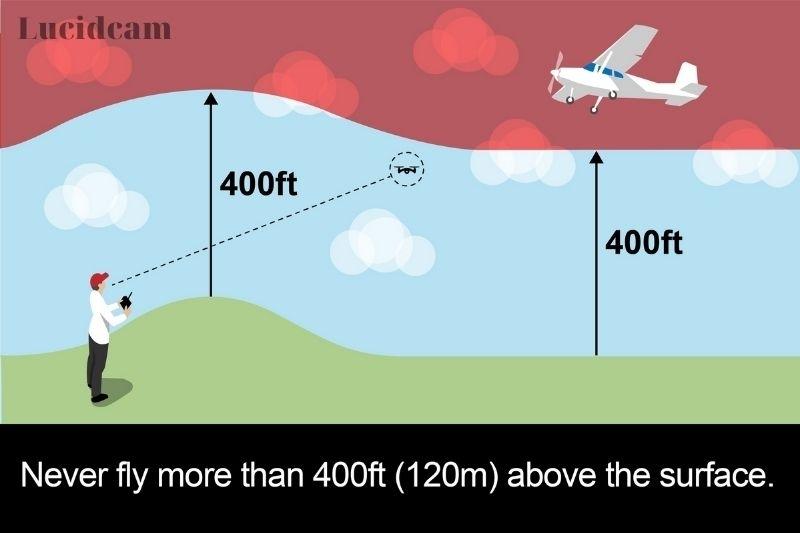
The 400-foot rule is a well-known and essential regulation for drone pilots to follow when flying their drones. The rule states that a drone should not fly higher than 400 feet above ground level (AGL) unless it is within 400 feet of a structure, such as a building or tower. This rule is based on safety concerns and the need to prevent collisions with manned aircraft.
The 400-foot rule is grounded in the Federal Aviation Administration’s (FAA) regulations, which govern the operation of drones in the United States. The FAA has established this rule to ensure the safety of all airspace users and prevent conflicts between drones and manned aircraft. Drones that fly above 400 feet AGL can potentially enter the airspace of manned aircraft, which poses a significant risk to pilots and passengers.
The 400-foot rule also takes into account the limited capabilities of drones. Most drones are not equipped with technology to detect and avoid manned aircraft, making it essential for pilots to maintain a safe distance from them. Additionally, flying too high can cause drones to become unstable and more susceptible to weather conditions, resulting in a higher risk of crashes.
What Is The Limit At 400 Feet?

The 400-foot limit is a critical safety regulation set by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) for commercial and recreational drone operators. This limitation is in place to ensure that drones do not interfere with manned aircraft, which typically fly at altitudes ranging from 500 to 40,000 feet. The 400-foot rule is a part of the FAA’s Part 107 regulations that govern the commercial use of drones. These regulations set guidelines for the operation of drones for commercial purposes, including the altitude limitations.
The 400-foot rule is designed to provide a safety buffer between unmanned aircraft and manned aircraft. By staying below 400 feet, drones are unlikely to pose a hazard to airplanes, helicopters, and other crewed aircraft. Additionally, this altitude limit helps prevent collisions with buildings, power lines, and other obstacles.
It’s important to note that commercial drone pilots can fly above 400 feet if they obtain a waiver from the FAA. In order to receive a waiver, pilots must demonstrate that their flight will not pose a risk to other aircraft or people on the ground. For hobbyist drone pilots, the 400-foot limit is not negotiable, and they must always keep their drones at or below this altitude.
What are the rules for drone pilots who are professional or recreational?
Because it is simpler, let’s start with the altitude rule that recreational drone pilots must follow. Before the FAA Reauthorization Act of 2018, the rules that governed recreational drone flight was simply called “guidelines,” making them prone to non-compliance. The FAA Reauthorization Act of 2018 made it mandatory to implement the rules.
The new rules included a 400-foot limit in uncontrolled airspace and a blanket restriction in controlled airspace. Although there are now options to request authorization to fly uncontrolled airspace, it is not possible to get a waiver for the 400-foot rule. Recreational drone pilots are not permitted to fly in uncontrolled airspace.
Part 107 commercial drone pilots are subject to the same rules, with one important difference. A pilot may fly their drone over 400ft if it is within 400 feet of a structure.
This exception was created so commercial drone pilots could offer inspections of skyscrapers, cell towers, and industrial equipment. These tall structures can still be cleared by manned aircraft, so it is perfectly acceptable for drones to fly around them at higher altitudes. These situations can also be handled by licensed drone pilots.
Are There Drones That Prohibit You From Flying Higher Than 400 Feet?
Yes, there are drones that come with built-in altitude limits that prohibit you from flying higher than 400 feet. These limits are often set by the drone’s manufacturer or by the software that controls the drone’s flight.
For instance, DJI, one of the largest drone manufacturers in the world, has set a default altitude limit of 120 meters (approximately 394 feet) for many of its drones. This means that if you try to fly your DJI drone higher than this limit, it will automatically stop ascending and remain at the maximum height.
However, some drones allow you to adjust the altitude limit through their accompanying software. For instance, DJI’s Go 4 app allows users to set a maximum altitude up to 500 meters (approximately 1,640 feet), which exceeds the 400-foot limit set by the FAA for recreational and commercial drone use.
Nevertheless, it is important to note that flying above the 400-foot limit without proper authorization from the FAA is illegal and can result in hefty fines or even criminal charges.
Furthermore, some drones have built-in safety features that prevent them from flying higher than the 400-foot limit, regardless of the software settings. For example, the DJI Mavic Air 2 and Mavic 2 Pro both have an upward-facing obstacle avoidance system that will prevent them from flying above 400 feet if they detect a ceiling or other obstacle in their path.
In conclusion, while some drones may allow users to adjust the altitude limit beyond 400 feet, it is important to always adhere to FAA regulations and fly within the legal limits. It is also important to check the drone’s specifications and features to ensure that it has the necessary safety features to prevent flying beyond the legal limit.
Are you allowed to fly above 400 feet?
In most cases, no, you are not allowed to fly above 400 feet with a drone. The 400-foot limit is set by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States and is designed to keep drones at a safe distance from manned aircraft. It’s also important to note that the 400-foot limit applies to all drones, including those used for commercial purposes.
There are some exceptions to the 400-foot rule. For example, commercial drone pilots can fly higher than 400 feet if they obtain a waiver from the FAA. In order to obtain a waiver, the pilot must demonstrate that they can safely operate the drone at a higher altitude and must provide a detailed plan for the flight.
Hobbyist drone pilots, on the other hand, are not able to obtain waivers to fly above 400 feet. They must stay within the 400-foot limit at all times. Violating this rule can result in fines and other penalties.
It’s also important to note that the 400-foot limit is not the only rule that drone pilots must follow. They must also avoid flying near airports, stay away from other aircraft, and follow all other FAA regulations. By following these rules, drone pilots can operate their aircraft safely and responsibly, while also minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Can A Drone Be Flown Above 400 Feet Legally?

This question is frequently asked by drone pilots all around the globe. It is legal to fly a drone over 400 feet. This is dependent on a few things.
If you are above a specific structure’s highest limit:
This information is vital for a drone pilot who wants to capture HD shots of buildings or areas at a height greater than 400 feet.
You can hover above a building or structure if you want to fly above it. Usually, this is 400 feet higher than the highest point.
If you are within 400 feet of a structure:
You can fly your drone within 400 feet of any structure or building, but you are not allowed to fly it beyond 400ft.
The FAA understands that commercial drones can be used for film and photography purposes.
Keep in mind that a building’s 400-foot radius is the limit of your freedom. You can fly anywhere you like as long as it is uncontrolled and where there is less aircraft traffic.
Authorization and License:
To fly in controlled airspace, you will need a registration and a license to exceed the 400-foot altitude limit.
To obtain a license for unrestricted drone flying, make sure to contact the authorities we have mentioned.
Avoid manned aircraft and restricted airspace. Any accidental or reckless collision could be very detrimental to your drone piloting skills.
What Are The Penalties For Flying Your Drone Above 400 Feet?

If you fly your recreational or commercial drone at an altitude that exceeds the limit, there are severe penalties. The FAA classifies drones as unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) according to their classification.
Here are some possible penalties and problems if you fly your drones higher than 400ft.
Monetary Fines
You could be fined up to a certain amount depending on how dangerous or problematic your flight was.
A general violation can result in a monetary penalty of $100 to $200. If your drone flight causes a problem for other manned aircraft, you could face severe penalties of up to a thousand dollars.
Criminal Convictions
Any violation of the rules and regulations regarding drone flight could result in criminal charges.
Although it is uncommon, this can happen if someone is reckless in controlled airspace. This is because the air traffic is more than the traffic in uncontrolled areas.
Revocation of Pilot’s License/Authorization:
If someone is flying drones in controlled areas above 400 feet, the FAA can suspend or remove any type of pilot’s authorization.
They can also cancel an application for a pilot’s license for up to a year, so drone pilots won’t be able to risk any manned aircraft in controlled space because of their reckless or suspicious piloting.
If you are interested in knowing more information, check out Do You Need A Pilot’s License To Fly A Drone 2023: Top Full Guide
FAQs
Can the FAA track my drone?
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), just before Christmas, published a proposal that would enable them to track almost every drone flying in US airspace.
What is the legal maximum you can fly a drone at?
400 feet above ground is the maximum allowed altitude. If your drone stays within 400 feet of any structure, it can go higher. The maximum speed is 100 mph (87 kph).
Are drones visible on the radar?
Radar is capable of detecting drones that have a larger RCS. This allows them to be detected at greater distances than a drone that has a smaller RCS. For Phantom 4 size drones, radar systems are capable of detecting drones as far as 1 mile away. The size of the drone can affect the range. Weather conditions such as rain or fog can also affect radar detection range.
Conclusion
Drone communities continue to debate the altitude limit for drone flight. This “guideline” was once a suggestion for recreational drone pilots. Now, they must follow the new regulations without exception. Part 107-licensed drone pilots, on the other hand, are expected to adhere to this rule to the letter. However, they have the option of a few exceptions under certain conditions.
You may have noticed a firmware-bound function that limits the drone’s altitude. This feature is available from most reputable brands. The limit isn’t fixed – almost all drones allow you to change it, perhaps in anticipation of professional drone pilots who may need the flexibility.
Lucidcam hopes this article will be helpful for you. Please share this post if you found it helpful so that others might see its contents as well! Thank you for reading!
